Automation control refers to the use of control systems and technology to automate and manage various processes and operations in industrial, manufacturing, and other domains. It involves the integration of hardware and software components to monitor, control, and optimize the performance of machines, equipment, and systems.
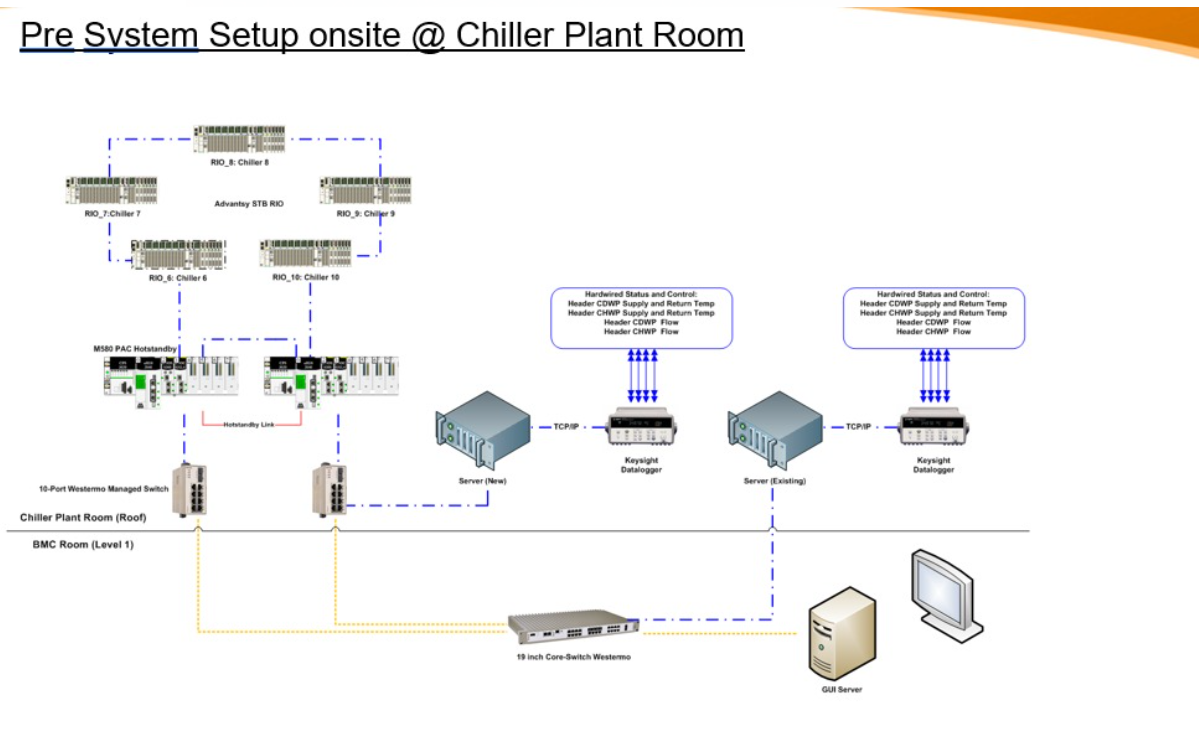
Key Aspects of Automation Control:
Control Systems: Automation control systems utilize control devices and equipment to regulate and supervise processes.
Benefits of Automation Control:
a. Improved Efficiency: Automation control optimizes processes, reduces manual intervention, and minimizes errors, leading to increased productivity and operational efficiency.
b. Enhanced Safety: Automation control systems can incorporate safety features, such as emergency shutdowns, alarm systems, and fault detection mechanisms, to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment.
c. Consistency and Quality: Automation control systems enable precise control and monitoring, ensuring consistent product quality and reducing variability in manufacturing processes.
d. Remote Monitoring and Control: Automation control systems allow for remote monitoring and control of processes, enabling real-time decision-making, diagnostics, and troubleshooting from any location.
e. Cost Savings: Automation control can reduce operational costs by minimizing waste, optimizing energy consumption, and improving resource utilization.
f. Scalability and Flexibility: Automation control systems can be scaled up or modified to accommodate changes in production requirements or process parameters.
Automation control plays a crucial role in modern industries by enabling efficient and reliable operation, improving safety, and facilitating continuous improvement. It empowers organizations to streamline processes, achieve higher productivity, and adapt to changing market demands.



