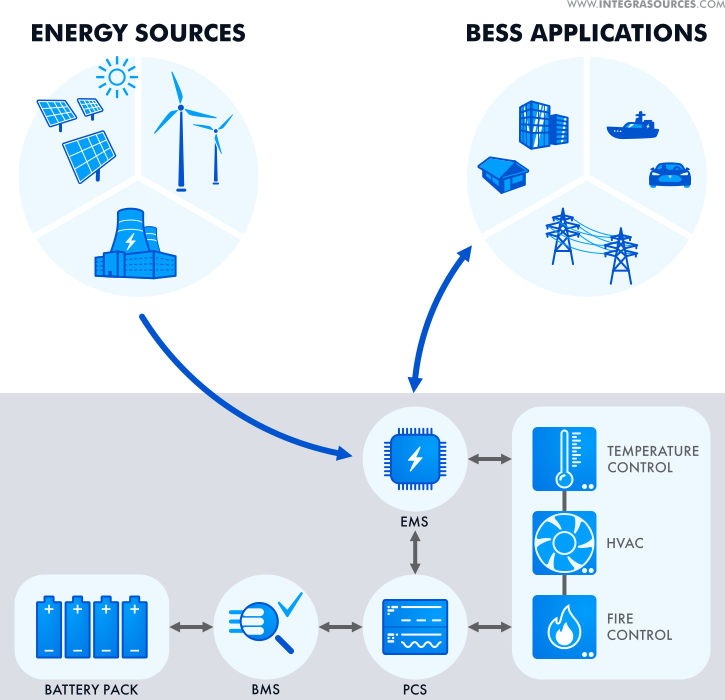
A battery energy storage system (BESS) is a technology that stores electrical energy in batteries for later use. It involves the use of rechargeable batteries to store excess electricity generated from various sources, such as renewable energy systems, grid power during off-peak periods, or during times of low demand. The stored energy can be discharged back into the grid or used on-site when needed.
Load Shifting:
Excess energy generated during off-peak periods can be stored in batteries and discharged during peak demand periods, reducing the strain on the grid and avoiding peak-time electricity costs.
Renewable Integration:
Battery energy storage systems facilitate the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, by storing excess energy and delivering it when renewable generation is low or unavailable.
Grid Stabilization and Ancillary Services: Battery systems can provide ancillary services to the grid, such as frequency regulation, voltage support, and grid stabilization. They can respond quickly to fluctuations in supply and demand, helping maintain grid reliability and stability.
Backup Power:
Battery energy storage systems can provide backup power during grid outages or emergencies, ensuring uninterrupted power supply for critical loads.
Microgrid Support: Battery systems can be integrated into microgrids, providing energy storage and enhancing grid resilience, self-sufficiency, and the integration of renewable energy sources.



